PRODUCER CONSUMERS PROBLEM
Problem
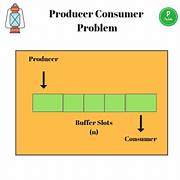
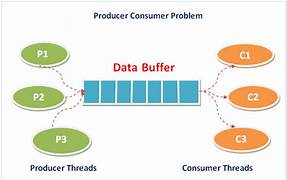
The producer-consumer problem is an example of a multi-process synchronization problem. The problem describes two processes, the producer and the consumer that shares a common fixed-size buffer use it as a queue. The producer’s job is to generate data, put it into the buffer, and start again. At the same time, the consumer is consuming the data (i.e., removing it from the buffer), one piece at a time.
Solution:
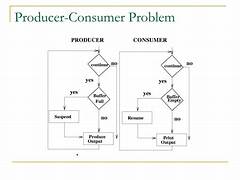
The producer is to either go to sleep or discard data if the buffer is full. The next time the consumer removes an item from the buffer, it notifies the producer, who starts to fill the buffer again. In the same manner, the consumer can go to sleep if it finds the buffer to be empty. The next time the producer puts data into the buffer, it wakes up the sleeping consumer.
approach
When producer produces an item then the value of “empty” is reduced by 1 because one slot will be filled now. The value of mutex is also reduced to prevent consumer to access the buffer. Now, the producer has placed the item and thus the value of “full” is increased by 1. The value of mutex is also increased by 1 because the task of producer has been completed and consumer can access the buffer.