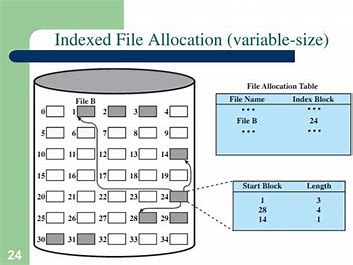
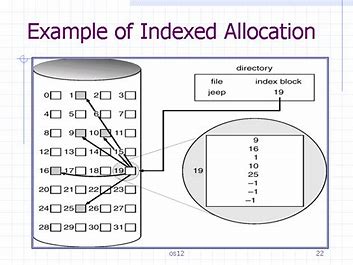
INDEXED FILE ALLOCATION
INDEXED
Because the file blocks are distributed randomly on the disk, a large number of seeks are needed to access every block individually. This makes linked allocation slower. It does not support random or direct access. We can not directly access the blocks of a file. A block k of a file can be accessed by traversing k blocks sequentially (sequential access ) from the starting block of the file via block pointers. Pointers required in the linked allocation incur some extra overhead.
Advantages
This supports direct access to the blocks occupied by the file and therefore provides fast access to the file blocks. It overcomes the problem of external fragmentation.
Disadvantages
The pointer overhead for indexed allocation is greater than linked allocation. For very small files, say files that expand only 2-3 blocks, the indexed allocation would keep one entire block (index block) for the pointers which is inefficient in terms of memory utilization. However, in linked allocation we lose the space of only 1 pointer per block.