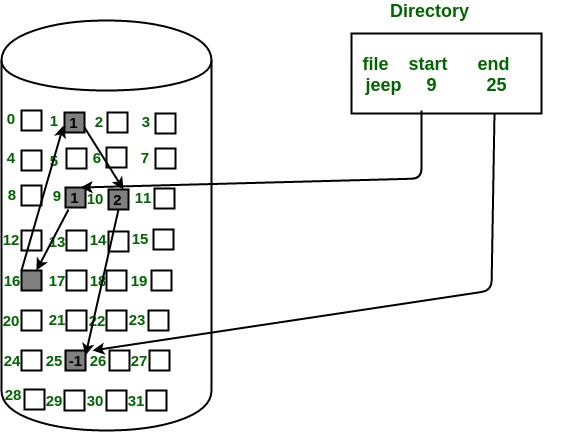
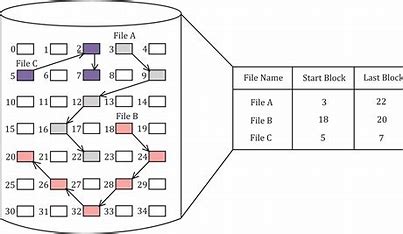
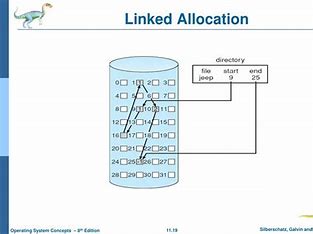
LINKED FILE ALLOCATION
Linked
This method suffers from both internal and external fragmentation. This makes it inefficient in terms of memory utilization. Increasing file size is difficult because it depends on the availability of contiguous memory at a particular instance.
Advantages
This is very flexible in terms of file size. File size can be increased easily since the system does not have to look for a contiguous chunk of memory. This method does not suffer from external fragmentation. This makes it relatively better in terms of memory utilization.
Disadvantages
Because the file blocks are distributed randomly on the disk, a large number of seeks are needed to access every block individually. This makes linked allocation slower. It does not support random or direct access. We can not directly access the blocks of a file. A block k of a file can be accessed by traversing k blocks sequentially (sequential access ) from the starting block of the file via block pointers. Pointers required in the linked allocation incur some extra overhead.